LMS: A Guide for Learning Management Systems
Technology and it’s branches have definitely affected every industry, new and old. Industries that had previously resisted innovation have started to introduce tech into specified departments, after which they’ve fully embraced its usage after witnessing the growth and profit they reap out of it. One such sector is education, where teachers and students have learned to grow together by implementing software's and gadgets that make learning fun. These innovations find their use cases in a lot of scenarios, including managing and hosting data for both students and teachers to interact with. Yes, I am talking about a management system, and yes, I will answer all your questions by the end of this article.

What on earth is an LMS?
Before we go any further into the components, use cases, benefits, etc. of a Learning Management System, we’ll answer the most basic of questions, being what exactly it is. LMS stands for a learning management system, which is a pretty simple acronym with a pretty clear motive. It’s called a Learning management system because it helps you organize courses (create, change, assign, grade, etc.) in order for you to deliver that content to learner’s within your reach. This software caters to eLearning courses, and helps you manage them. So, just like an answer to a description question, we’ll move over to what it’s comprised of. It’s made up of 2 essential components:
A server component, that deals with the core functionality (creating, managing, and delivering courses, authenticating users, serving data and notifications, etc), and
A user interface that runs inside your browser as a web, that is used by administrators, instructors and students.
There are a lot of people and businesses that utilise LMS, as many of them use eLearning to educate students and employees alike.
What can an LMS be used for?
As an eLearning platform, many organizations both big and small, can utilize the LMS for all kinds of learning activities. A few of its use cases are:
Employee Training
The need to train employees both new and existing in new skills is a constant in any organizations that differ in terms of background. An LMS helps to cut down costs and eliminate business disruptions associated with traditional learning, by letting employees study the material online and at their own pace. These also help give administrators a better insight on the progress of their learners with the help of the assorted monitoring and reporting tools.
Employee Orientation
The task-heavy duty of on-boarding a new hire can also be automated and handled by an LMS. The on-boarding course would include less-interesting matter that nobody pays attention to (company's history, CEO's message) as well as the all-important detailing of their roles and responsibilities, information about career advancement opportunities and benefits.
Knowledge Retention
Learning has always been a two-way process. In the process of training your learners, you need to ensure that you in turn learn from them. The knowledge retention program does just that, where the program ensures that valuable skills, techniques and information stays with your company when your employees leave or retire.
Education
The entire point of an LMS is to offer general educational requirements (duh!). This is also why schools selling online lessons, a traditional educational institution supplementing its classroom-based courses, a business educating its clients, or even a government agency or NGO helping educate the general population.

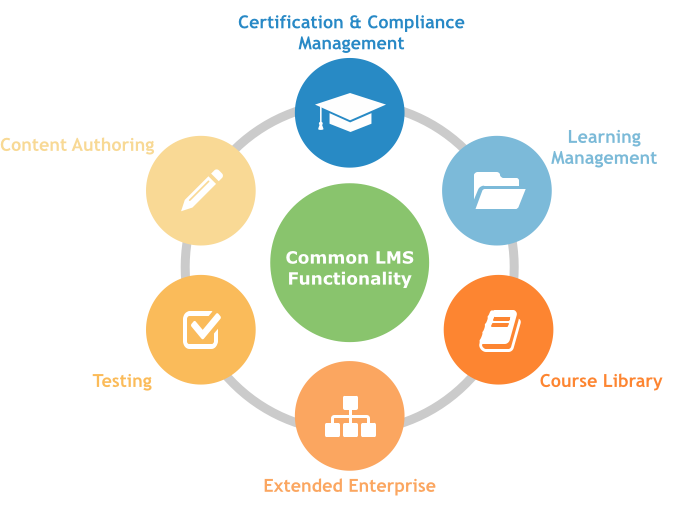
What are its Functionalities?
As mentioned above, an LMS handles the management and delivery of eLearning courses. Here's a brief:
-
Creating an eLearning course. You'll be needing content to actually deliver to your learner base. This can be achieved by either creating your course material from scratch (by writing your lessons' content inside the LMS), or by importing existing material. Advanced LMS software, like TalentLMS, lets you add course material from various sources and in different formats, and even allows you to incorporate multimedia files (video, audio, graphics, etc.)
-
Organizing your Courses. Once you're done creating courses, you'll need to organize them into groups, such as a module. This process could be as simple as offering a single course, or as complicated as having multiple courses, departments and student groups operating across several branches. An LMS, gives you a set of organizational tool (courses, groups, categories, skills, branches, etc.) that you can combine in multiple ways and have the ultimate flexibility in how you deliver your lessons.
-
Delivering your Courses. After you've created and organized your courses, you would be ready to deliver them to your students. A modern LMS should handle cases where they might be needed for a small group of employees within a company, or for a bigger student base. They could also be delivered as free or paid courses. These should also be able to cater to mobile devices.
-
Managing users. The ability to manage courses and users gives you the Management in LMS. There are generally 3 kinds of users: administrators (people that set up and configure your LMS), instructors (people that teach or prepare lessons for the LMS), and of course, learners. Administrators and instructors could be the same, while learners could be employees or students enrolled for you course. Managing basically involves registering users, assigning them courses, interacting with them either as a instructor or administrator, determining content restriction, handling payments (in case of paid courses), grading and conference sessions.
-
Monitoring and Assessing student progress. An LMS gives you an automated and quick access to course enrollment statistics, attendance records, student grades and many other performance parameters. It should also include real-time alerts and notifications, reporting graphs and charts on cue, and spotting trends and issues.
-
Advanced LMS Features. Advanced features could include the ability to organize and hold eConference and hold eConference sessions, with multiple students participating through audio and video, online whiteboard functionality, so instructors and students can create and share writings and drawings in real time, ability to sell courses and integrate with payment processors and third party system integration. These can also be deployed locally, private cloud and cloud based.
Related links:
